Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Horai, Sawako*; Murakami, Shoichi*; Sakoda, Akihiro; Nakashita, Rumiko*; Kunisue, Tatsuya*; Ishimori, Yuu
Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 194(6), p.415_1 - 415_25, 2022/06
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:43.07(Environmental Sciences)This study conducted an investigation of trace element behavior at a former uranium (U) mining site and evaluated environmental impacts to biota. Concentrations of trace elements were determined in sediments, water, and three organism types (insects, frogs, and newts) from three zones in the former U mining site. Concentrations of As and U in the sediments and water samples were the highest at the mill tailings pond site, where post-U extraction remnants have been accumulated. Additionally, among the organisms analyzed the highest levels of these elements/isotopes were found in newts from MP. Considering data analyses of the whole-body element concentrations, bioaccumulation factors, and 
 N values for the organisms, it was concluded that newts might be the most vulnerable species in this location. Further monitoring and more accurate evaluation of the ecological impacts are preferred for this former U mining site.
N values for the organisms, it was concluded that newts might be the most vulnerable species in this location. Further monitoring and more accurate evaluation of the ecological impacts are preferred for this former U mining site.
Tanaka, Hiroshi; Sakoda, Akihiro; Ando, Masaki; Ishimori, Yuu
Hoken Butsuri, 51(2), p.107 - 114, 2016/06
Ambient dose rates are continuously monitored in Ningyo-toge Environmental Engineering Center, Japan Atomic Energy Agency. The present study discussed the variations in ambient dose rates, observed from April 2014 to March 2015, due to snowfall as well as rainfall. It is much snowy as one of climatic features in this area. Rain or snow was sampled for a certain period in the day of interest (17 cases in total), and then the concentration of radon progeny was measured. With the measured data, the variation in ambient dose rate was calculated considering the accumulation of the radon progeny on the ground. As a whole, this calculation was found to reasonably reproduce the time trends of observed dose rates, except for four cases. Based on the backward trajectory analysis, it was explained that the discrepancy in two cases out of the four was induced by changes of radon progeny concentration in precipitation around sampling period. It was suggested that the other two cases were caused by the run-off of rain from the ground surface.
Jiang, Q.*; Tamura, Kenji*; Asano, Maki*; Fukuyama, Kenjin*; Yamaji, Keiko*
no journal, ,
This study was conducted to understand the soil macro and micromorphological characteristics on the former open pit mining area of Ningyo-toge mine. The vegetation succession of the area has not progressed. Its dominant vegetation has been 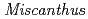 . The conclusions of this study are follows. The BC horizon of Site B has a lower Eh, which may be due to the less voids in the underlying soil, which results in seasonal accumulation of water. The contents of Mn, Cd, Pb, and Co were higher than the average contents in Japanese soil, but they did not reach the level of pollution. The content of acid-soluble Fe was very low in the soil, Fe mainly is the form of residual and a part of reducible form in the study site. But, the content of Mn in acid-soluble form is high, and Mn has a greater impact on vegetation. In this study site, external human factors have a large influence, mixed with a large amount of black residue and wood chips. And the 0-5cm of soil is in good structure, but the soil in the lower layer is not fully developed and it is a block structure.
. The conclusions of this study are follows. The BC horizon of Site B has a lower Eh, which may be due to the less voids in the underlying soil, which results in seasonal accumulation of water. The contents of Mn, Cd, Pb, and Co were higher than the average contents in Japanese soil, but they did not reach the level of pollution. The content of acid-soluble Fe was very low in the soil, Fe mainly is the form of residual and a part of reducible form in the study site. But, the content of Mn in acid-soluble form is high, and Mn has a greater impact on vegetation. In this study site, external human factors have a large influence, mixed with a large amount of black residue and wood chips. And the 0-5cm of soil is in good structure, but the soil in the lower layer is not fully developed and it is a block structure.